Is your network struggling to keep up with increasing data demands without expanding the costly fiber infrastructure? The 100G CWDM QSFP28 module provides an innovative alternative by effectively multiplying data capability through a limited number of fibers. Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing enables multiple 100G channels to be established on few fibers. With this design, the user benefits from saving money and simplifying the network design. Read on to discover how 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules efficiently use fiber, manage costs, and scale metro and enterprise backbone networks. After your reading, you will be prepared to choose the best module for a configuration that will fit your individual network requirements and constraints.

100G CWDM QSFP28 Modules: Why They Are the Optimal Choice for Metro and Enterprise Backbone Networks
Cisco’s 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules offer a powerful solution to use as much fiber as possible without sacrificing speed. Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) intelligence transmits many 100G channels over a finite number of fiber strands. CWDM is like turning a single highway into multiple lanes, where each lane uses a different color of light as a separate highway—the end result is that the capacity is dramatically increased without the need to lay new fiber.
100G CWDM QSFP28 modules have their own advantages over both Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) or standard QSFP28 modules in terms of costs added, resource savings, and fiber utilization. On one hand, DWDM has more channel density, but typically at higher costs and increased complexity. CWDM is a middle-of-the-road solution for operator preference on ease of use and cost-effective multiplexing tailored for metro and enterprise backbone networks that look to maximize both performance and scalability.
Deployment Simplicity and Integration
Deploying 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules is quite simple and likewise integrates directly into all current fiber infrastructure. Many supplier equipment is 100G compliant, and fiber connections available from existing or preferred suppliers can allow new installations with little to no downtime and stretch the scalable options if required by answering the demand for more traffic. Network operators can add channels when traffic volumes warrant increasing fiber utilization without major upgrades.
Feature Comparison
| Feature | DWDM QSFP28 | Standard QSFP28 | 100G CWDM QSFP28 |
| Channels per fiber | 40+ (Dense) | 1 | Approximately 8 (Coarse) |
| Deployment complexity | High | Low | Medium |
| Fiber resource utilization | Efficient but complex | Low | Highly efficient |
| Cost | High | Moderate | Cost-effective |
| Ideal use case | Long-haul, high-capacity | Short-range, simple | Metro and enterprise backbone |
Benefits of Incorporating 100G CWDM QSFP28 Modules
Incorporating 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules into the business allows companies to optimize their fiber assets, manage costs, and build future-proof networks, which is why 100G CWDM technology is the right decision for purposeful metro and enterprise backbone environments.
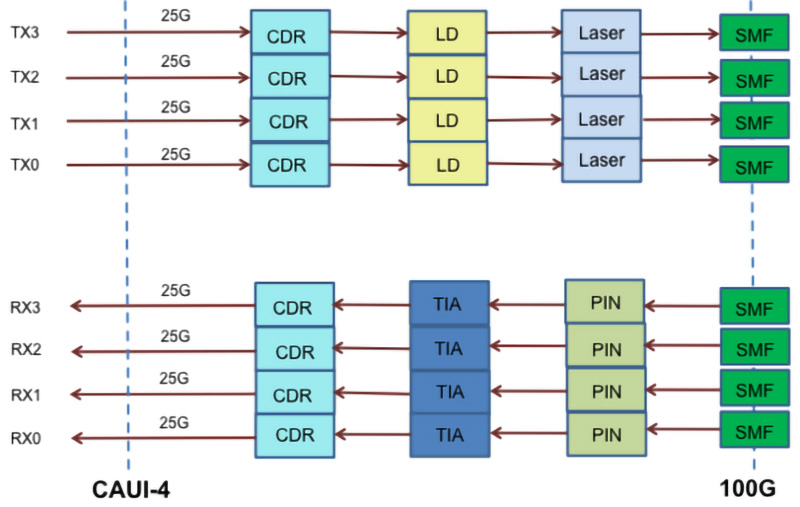
100G CWDM QSFP28 Technology Deep Dive and Informed Selection Framework
To grasp the technological basis of 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules, I feel it is important to understand that CWDM, or Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing, is a way to take advantage of distinct wavelengths, which are located more widely spaced on the light spectrum, so we are able to multiplex and carry multiple signals on a single fiber. CWDM successfully reduces interference from each wavelength, and this gives us a simpler design than DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing). A 100G QSFP28 typically has CWDM wavelengths from approximately 1270 nm up to 1610 nm, and out of that range, you can typically consider these wavelengths for CWDM channels, with 20 nm spacing between channels. Each wavelength is a different channel carrying 100G data streams. The following table outlines the CWDM wavelengths that are typical of a QSFP28:
CWDM Channel Table
| Channel Number | Wavelength (nm) | Frequency (THz) | Typical Use Case | Compatible Fiber Type | Max Transmission Distance |
| 1 | 1270 | 236.22 | Short-range intra-data center | Single-mode / Multimode | Up to 20 km |
| 2 | 1290 | 232.56 | Metro network links | Single-mode | Up to 40 km |
| 3 | 1310 | 229.10 | Enterprise campus backbone | Single-mode | Up to 40 km |
| 4 | 1330 | 225.56 | Metropolitan area network | Single-mode | Up to 60 km |
| 5 | 1350 | 222.22 | Regional network interconnect | Single-mode | Up to 60 km |
| 6 | 1370 | 219.00 | Long-haul network access | Single-mode | Up to 80 km |
| 7 | 1390 | 215.85 | Extended metro connections | Single-mode | Up to 80 km |
| 8 | 1410 | 212.77 | Backbone network | Single-mode | Up to 80 km |
Supported Protocols and Fiber Compatibility
Supported protocols of 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules include 100G Ethernet (IEEE 802.3bm), OTU4, and OTN, giving users extensive compatibility with various network configurations. Reach options usually range from 10 km – 80 km depending on the subtype of the module used and the fiber quality.
Fiber compatibility matters: multimode fibers can only go short distances and have high attenuation characteristics, while single-mode fibers can go a much greater distance and are preferred characteristics for metropolitan type networks.
Module Selection Guidance
When determining the appropriate 100G CWDM QSFP28 module, consider the required transmission distance, the number of channels needed, and the budget. Here is a decision tree to use for possible paths:
- If you need either short or medium distances (<20 km) and a fewer number of channels: use the lower cost modules that are optimized for multimode fibers.
- If you are in a metro backbone where a longer reach (20-80 km) is necessary and more channels are required: you can go to a higher performance module and work with single-mode fiber and CWDM MUX/DEMUX devices.
- If density and reach is heavily important to you and your budget allows it, you can try hybrid or DWDM solutions. But for most metro/enterprise backbones, CWDM reduces costs effectively and with efficiency.
Compatibility Considerations
Compatibility is also a very important variable in the CWDM 100G QSFP28 decision. The 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules must work with CWDM MUX/DEMUX devices that combine and separate wavelengths on the fiber line. Well known vendors like Cisco, Juniper, and Huawei have compatibility testing and certification allowing you to mitigate risks when mixing devices from various vendors. Always check the module firmware and hardware of the device version to ensure compatibility.
Parameter Overview
| Parameter | Range | Notes |
| CWDM Wavelength Range | 1270 nm – 1610 nm | 20 nm channel spacing |
| Supported Protocols | 100G Ethernet, OTU4, OTN | Broad compatibility |
| Transmission Distance | 10 km – 80 km | Dependent on fiber type and module selection |
| Fiber Type | Multimode (short reach), Single-mode (long reach) | Multimode suited for up to 10-20 km, single-mode for longer distances |
| Typical Power Budget | 12 – 16 dB | Varies by module and fiber quality |
Advantages of 100G CWDM QSFP28
With an understanding of these specifications and goals in mind, operators can assess the consequences of numerous 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules and decide the right choice; there are quite a few advantages, one of which is reliability through greater efficiency in expanding, decreased fiber counts, and a much smoother transition into and within the various existing metro and enterprise backbones.
100G CWDM QSFP28 Modules Product Lineup

BYXGD-QSFP28-100G-CWDM-2KM-LC: This module operates at 4×25.78G rate using CWDM over single-mode fiber, supports 2KM transmission, features EML laser, PIN receiver, >3.5 dB extinction ratio, and uses LC interface.
The Successful 100G CWDM QSFP28 Deployment
A major financial services company wanted to update the backbone network to accommodate multiple operating and application loads for additional data traffic without increasing the fiber footprint. They found keeping latencies low on mission-crucial transactions costly, and it deteriorated to operational levels.
They decided to layer 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules to support multiple 100G channels over the existing fiber links. In comparison with using the traditional duplex BIDI/GIGE methods, the 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules dropped the expense of fiber cabling by many factors, and value engineered to stay within existing costs.
The result of the changes was a 20% drop in network latencies because of the spatially reduced tail of fiber needed to support the traffic. Their reduced costs were in the range of 30% related to fiber purchase and labor costs. Their throughput was much higher, in the range of 40% or greater. Therefore, they improved their data flows to enhance service, which is critical for fast data requirements for real-time financial reporting timelines.
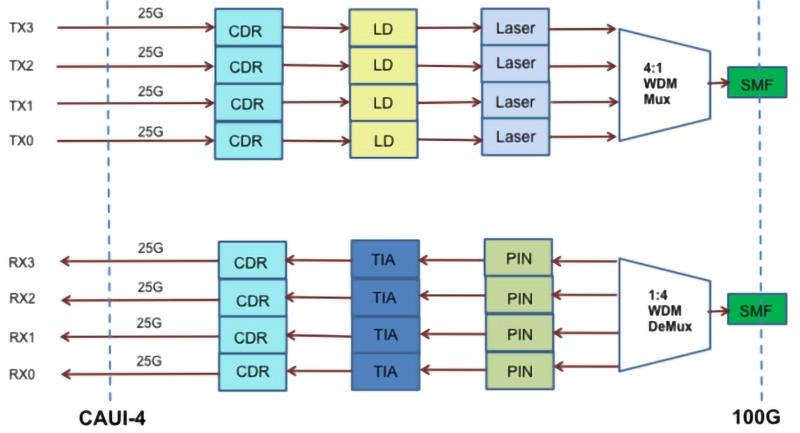
Deployment Considerations
Their focus for decisions was on ensuring the reach of the module was closely matched to the use of fiber, and that vendor-certified CWDM MUX/DEMUX was deployed to support. This would make them efficient in terms of time and ease of deployment. Some will say that the 100G CWDM modules, automated by definition, are open, and 100G CWDM modes were no different. They could grow their capacity over time with very little disruption to their existing footprint and, therefore, their continuity of business.
The deployment illustrated three areas of value for the 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules in terms of speed, cost savings, and scalability, all attractive elements when networks are enterprise backbone with expanding footprints.
OEM Versus Third-Party 100G CWDM QSFP28 Modules
Selecting between OEM and third-party 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules can have an impact on performance, costs, and subsequent service. Although independent testing showed that OEM modules were more reliable, had more consistent performance, and better integration of hardware with software, third-party modules may attract on price alone—as a value-based opportunity.
Performance testing indicated that OEM modules had less variation in data rate and lower error rates independent of network conditions. Conversely, it was evident that there were some sign-in glitches with many of the third-party modules that would cause high latency for all 100G devices and required small firmware updates as glitches occurred. The potential for these types of risks can result in hidden operational costs that offset any or all of the savings you may have realized when procuring the equipment.
Warranties and Service Considerations
Warranties and service are important considerations as well. OEM vendors typically provide long warranty terms with 24/7 technical service, while third-party vendors have short warranty terms with little or no service support, which is a source of risk for enterprise deployments. Additionally, it is worth understanding the brand reputation, responsiveness, and availability of the third-party vendor when looking at or considering a third-party module.
Summary of OEM and Third-Party Module Comparison
| Aspect | OEM 100G CWDM QSFP28 | Third-Party 100G CWDM QSFP28 |
| Performance | High stability, certified compatibility | Varies, occasional compatibility concerns |
| Price | Higher upfront cost | More cost-effective, lower initial investment |
| Warranty | Typically 3-5 years, with options for extension | Usually 1-2 years, with limited extensions |
| Technical Support | Comprehensive vendor support and service | Basic support; may lack rapid response |
| Risk | Minimal, certified for major vendor equipment | Potential for incompatibility and downtime |
Risk Management and Buying Recommendations
Addressing risks for third-party modules can involve lab testing, using reputable brand names, and verifying firmware when working with networking equipment. Typically, enterprises willingly accept some potential trade-offs on network stability for the financial savings presented by third-party modules.
Thus, OEM 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules work well in mission-critical metro and enterprise networks, in which performance is paramount, and expect comprehensive support. Meanwhile, third-party modules can sometimes work well in other less demanding environments or as cost-savings opportunities, but only with sufficient quality checks.
Being deliberate in your purchasing practices allows confidence that your enterprise is getting both high-capacity performance on your network and peace of mind to operate all day long.
Frequently Asked Questions
Standard single-mode fiber with LC connectors is the norm. Make sure the cables you are using support the distance you are installing and also support low attenuation in order to keep the quality of the signal intact.
Optical power budgets are determined by taking into account the transmitter output, along with fiber loss, losses from the connectors, and the receiver sensitivity. Proper power budget planning helps to avoid degraded signals.
There are some modules that use tunable optics which allow wavelength tuning (i.e., changing the wavelength of the optics) to optimize the usage of spectrum and to align channels with each other, thereby allowing greater flexibility in the network.
The development path for modulation technologies will enable greater spectral efficiencies in 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules. For example, technologies like PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) allow data rates to transpire faster while continuing to minimize the amount of bandwidth consumed.
Integration with 400G networks is ramping up. CWDM modules can now adapt easily to the scope of coexistence as they work in a more inclusive multi-rate architecture, which will support transitional scaling down the line.
Tunable optics are a technology gaining momentum. Tunable optics support end-user wavelengths to be adjusted remotely without human intervention. This allows for greater efficiency of the channel by minimizing human intervention in the network.
Clearly, experts are hypothesizing more advancements to come in the adoption of software-defined optics, which will allow configuration of module parameters to happen dynamically and automatically based on network performance during the application.
Network operators who can stay ahead of technology advancements are able to future-develop their architecture around them, along with continuous improvements to their network infrastructure.
Contact Us For The Best Solution
When adopting 100G CWDM QSFP28 modules, you have entered a paradigm of fiber optimization at low cost and scalable performance for metro and enterprise backbones. Work to leverage even more information from the additional specifications and utilize solid products to ensure success in deploying reliable high-speed networks. During your decision-making and consultation process, have confidence to explore and interrogate new options with your next upgrade.
